Understanding Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion in English
Newton’s 3 laws of motion in English are fundamental concepts in physics. They describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. Understanding these laws is crucial for anyone studying physics or engineering.
What are Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion?
Newton’s three laws of motion, published in 1687, form the foundation of classical mechanics. They explain how objects move and interact with forces. These laws are universally applicable, from the smallest particles to the largest celestial bodies. Let’s break down each law.
Newton’s First Law: The Law of Inertia
This law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Essentially, objects resist changes in their state of motion. This resistance to change is called inertia.
For example, a book on a table remains at rest unless someone picks it up (applies a force). A hockey puck on frictionless ice continues to move at a constant velocity unless it hits something or experiences friction.
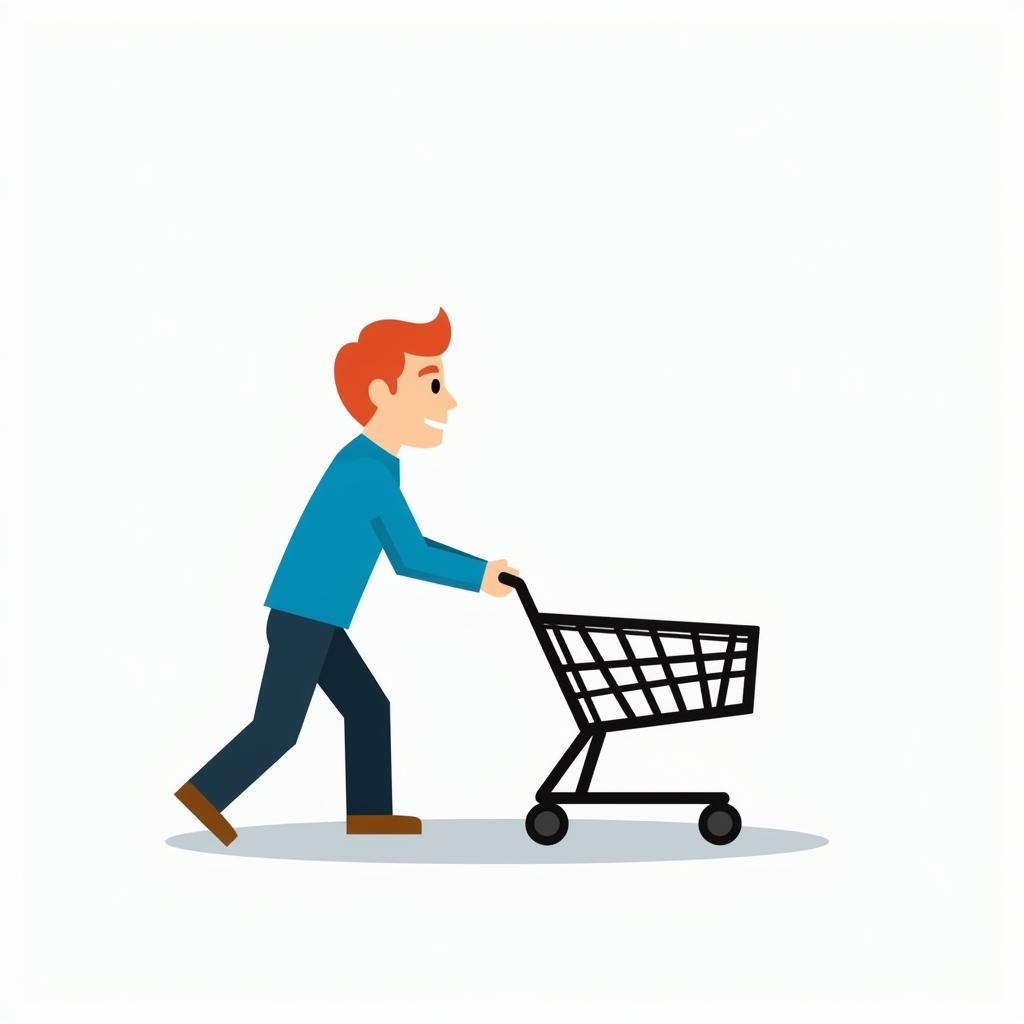
Newton’s Second Law: F=ma
This law defines the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to its mass. This is mathematically represented as F=ma, where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration.
 Newton's Second Law of Motion: F=ma
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F=ma
A simple example is pushing a shopping cart. The harder you push (greater force), the faster the cart accelerates. If the cart is full of groceries (larger mass), it will accelerate less for the same amount of force. ai phát minh ra định luật bảo toàn năng lượng provides a good parallel in understanding the concept of forces and their effects.
Newton’s Third Law: Action-Reaction
This law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object simultaneously exerts a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first object.
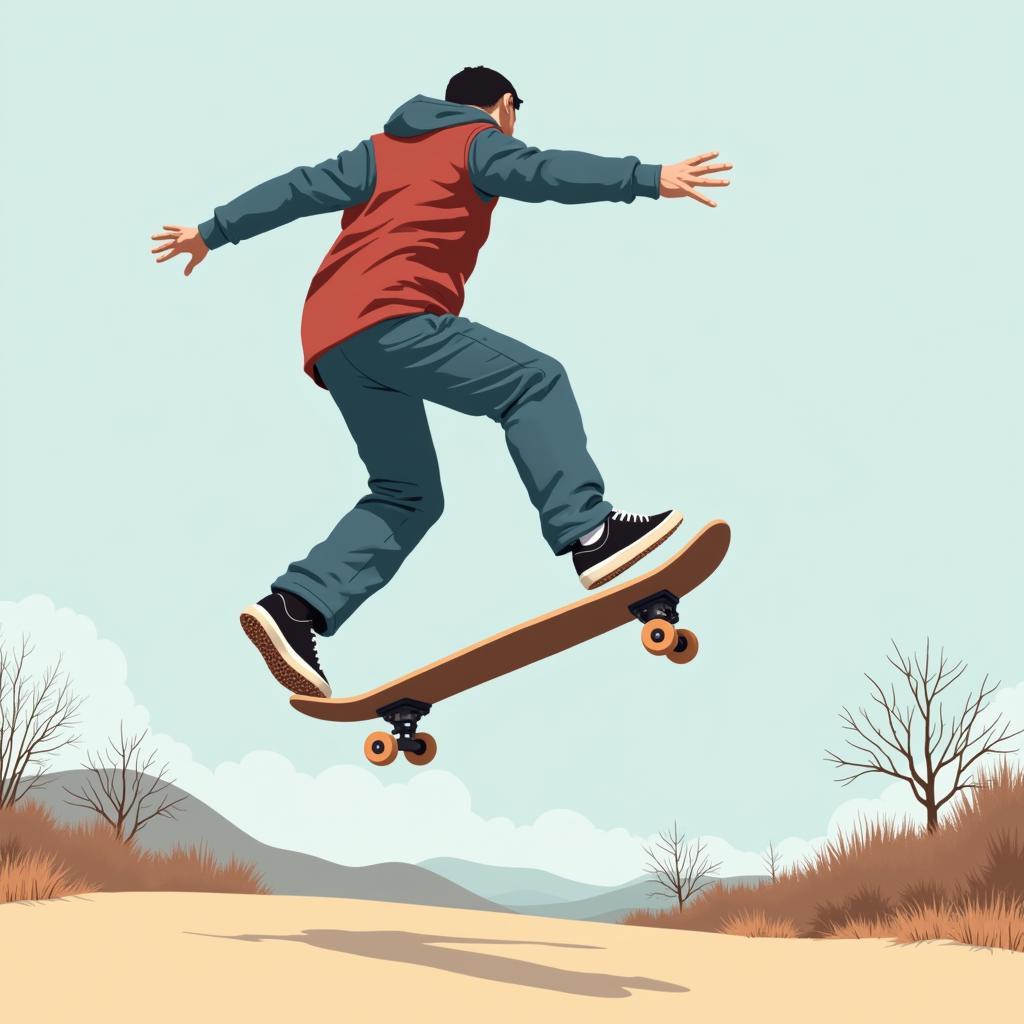 Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action-Reaction
Newton's Third Law of Motion: Action-Reaction
For instance, when you jump off a skateboard, you push backward on the skateboard (action). The skateboard, in turn, pushes you forward (reaction), causing you to move forward and the skateboard backward. Similar principles are discussed in bài tập nâng cao về các định luật bảo toàn.
Applying Newton’s Laws in Everyday Life
Newton’s laws are not just theoretical concepts; they govern the motion of everything around us. Understanding these laws helps us understand how cars move, how airplanes fly, and even how we walk. các định luật vật lý nổi tiếng explores other fundamental laws of physics that shape our understanding of the universe.
Conclusion
Newton’s 3 laws of motion in English are essential for understanding the physical world. They provide a framework for analyzing motion and the forces that cause it. By grasping these laws, we can better appreciate the intricate workings of the universe, from the simplest actions to the most complex phenomena. luật chiếu tướng trong cờ tướng may seem unrelated, but it also demonstrates the concept of action and reaction within a defined set of rules.
FAQ
- What is inertia?
- How is force related to acceleration?
- What is an example of Newton’s Third Law?
- Why are Newton’s laws important?
- How do Newton’s laws apply to everyday life?
- What is the formula for Newton’s Second Law?
- What is an unbalanced force?
Other Questions?
Need more help with legal issues in the gaming world? Check out chế luật giang hồ for a unique perspective.
Contact Us
For further assistance, please contact us:
Phone: 0903883922
Email: [email protected]
Address: Đoàn Thị Điểm, An Lộc, Bình Long, Bình Phước, Việt Nam.
We have a 24/7 customer support team ready to assist you.